Fiberglass post in dentistry
Often times the reconstruction of a tooth is a very difficult task to achieve if you do not have the support of a healthy dental tissue. What does that mean? When the destruction of a tooth is very large due to dental decay or to a fracture and there is nothing left but a few and very thin crown walls along with the root, we can not make a really stable and strong direct reconstruction .We need increased retention to obtin an enhanced resistance. For this reason, there is the solution of inserting posts in the root canal space.
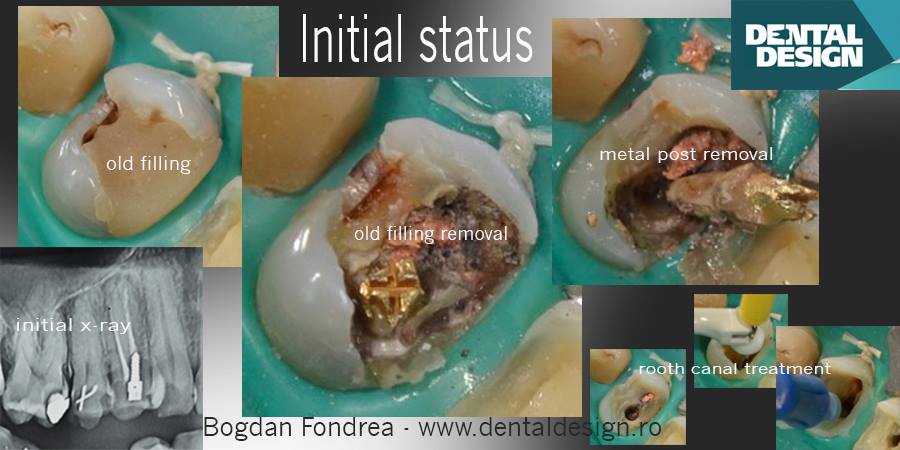
(first picture - old incorrect root canal treatment, cavity, bone infection and metal pin)
Initially, these posts ( called crown-root devices or pins) were metallic and sometimes they were prefabricated and inserted directly. Sometimes they were custom-made in a dental laboratory by a dental technician from a dental impression. Unfortunately, they had a lot of disadvantages like the considerable amount of coronal and radicular sound tooth structure that was sacrificed with increasing risk of root perforation and fracture.
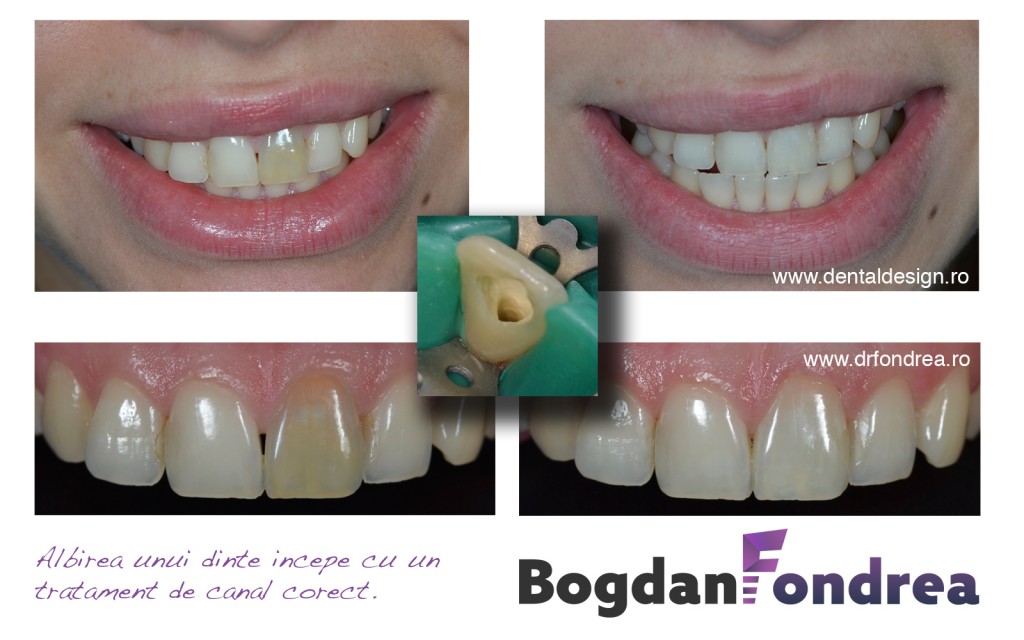
Improvements in composites and the development of dentine bonding systems have simulated a trend toward more conservative techniques of tooth restauration and so it began the use of the fiberglass posts system.
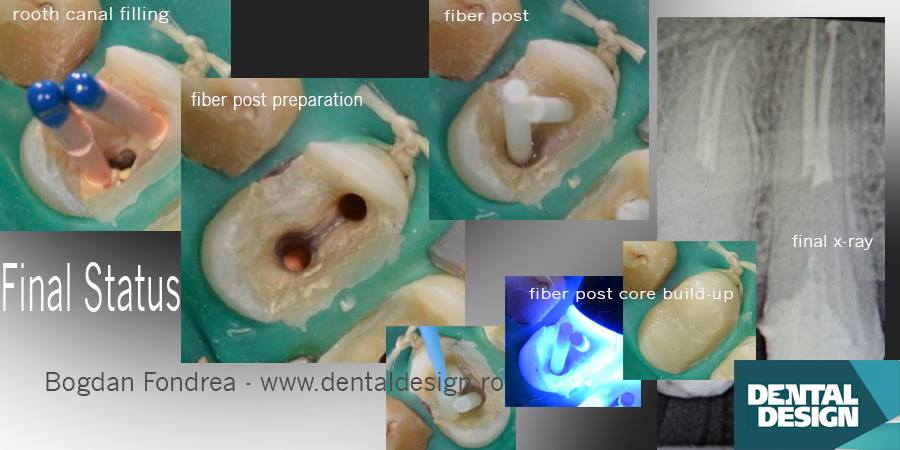
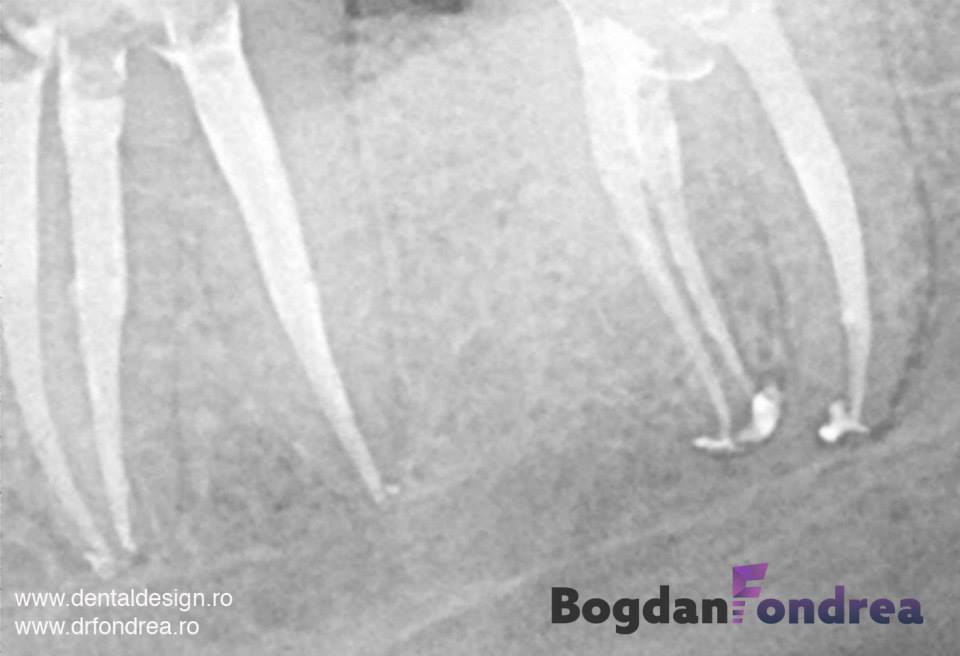
(second picture - new root canal treatment, no cavity, two fiberglass post core build up)
The similarity in the modulus of elasticity of fiberglass posts and resin cement with that of dentine have been advantageous in improving the performance of these kinds of restorations, compared with cast metal post and core restorations.
It is thought that fiber posts can distribute stresses between the post and dentine by their flexibility under load, resulting in favorable clinical behavior. Thus, if excessive forces are applied to the tooth, the post will be able to absorb them, reducing the possibility of root fracture.
Currently used fiberglass post systems are designed to be corrosion resistant, able to bond to tooth structure, esthetically pleasing, and to allow retrieval when the post core system fails.
Fiberglass is a biocompatible, inert, translucent, and durable material that includes free radicals that can form chemical connections.
They are easy-to-use, reliable, and cost-effective with a scientifically documented background. The time of work is reduced and the fiberglass post can be inserted in the same session with the root canal treatment. The tooth preparation is minimum (very low dental sacrifice) because the fiber post has only 1,2 - 1,50 mm diameter.
There are no allergic reactions to them and they are easily accepted by any pacient because no one likes to have something metallic in their mouth.
Stay strong, stay flexible! 🙂
Bogdan Fondrea & Denisa Sava - www.dentaldesign.ro